SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
Copyright (c) 2019-2020 Intel Corporation
- Smart Edge Open Network Edge: Offline Deployment
- Smart Edge Open support in offline environment
- Setup prerequisites
- Creating the offline package from an online node
- Placing the complete offline package in offline environment
- Deployment in offline environment
Smart Edge Open Network Edge: Offline Deployment
Smart Edge Open support in offline environment
The Smart Edge Open projects supports a deployment of the solution in an air-gapped, offline environment. The support is currently limited to “flexran” deployment flavor of Converged Edge Experience Kits only and it allows for offline deployment of vRAN specific components. Internet connection is needed to create the offline package, a script to download and build all necessary components will create an archive of all the necessary files. Once the offline package is created the installation of Converged Edge Experience Kits will be commenced as usual, in the same way as the default online installation would.
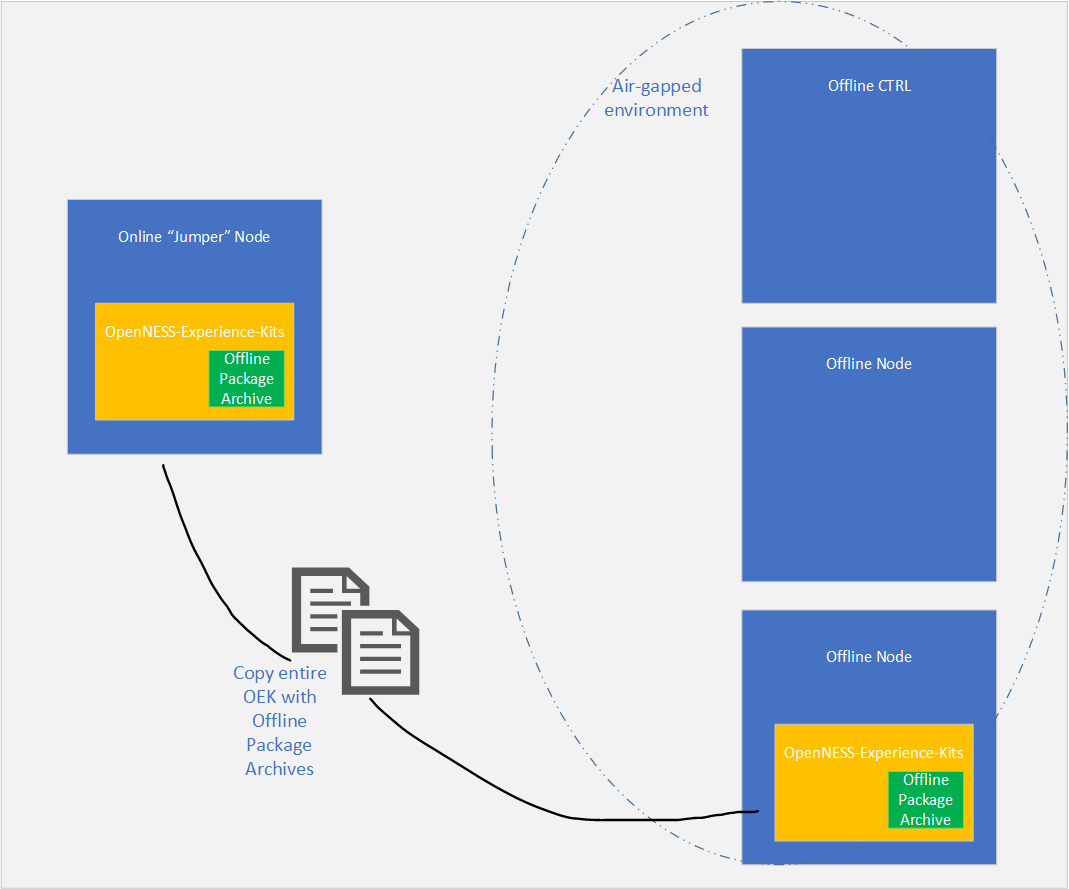
It can be deployed in two different scenarios. The first scenario is to deploy the Converged Edge Experience Kits from the online “jumper” node which is being used to create the offline package, this internet connected node must have a network connection to the air-gapped/offline nodes. The second scenario is to copy the whole Converged Edge Experience Kits directory with the already archived packages to the air-gapped/offline environment (for example via USB or other media or means) and run the Converged Edge Experience Kits from within the offline environment. All the nodes within the air-gapped/offline cluster need to able to SSH into each other.
Figure 1. Scenario one - online node connected to the air-gapped network
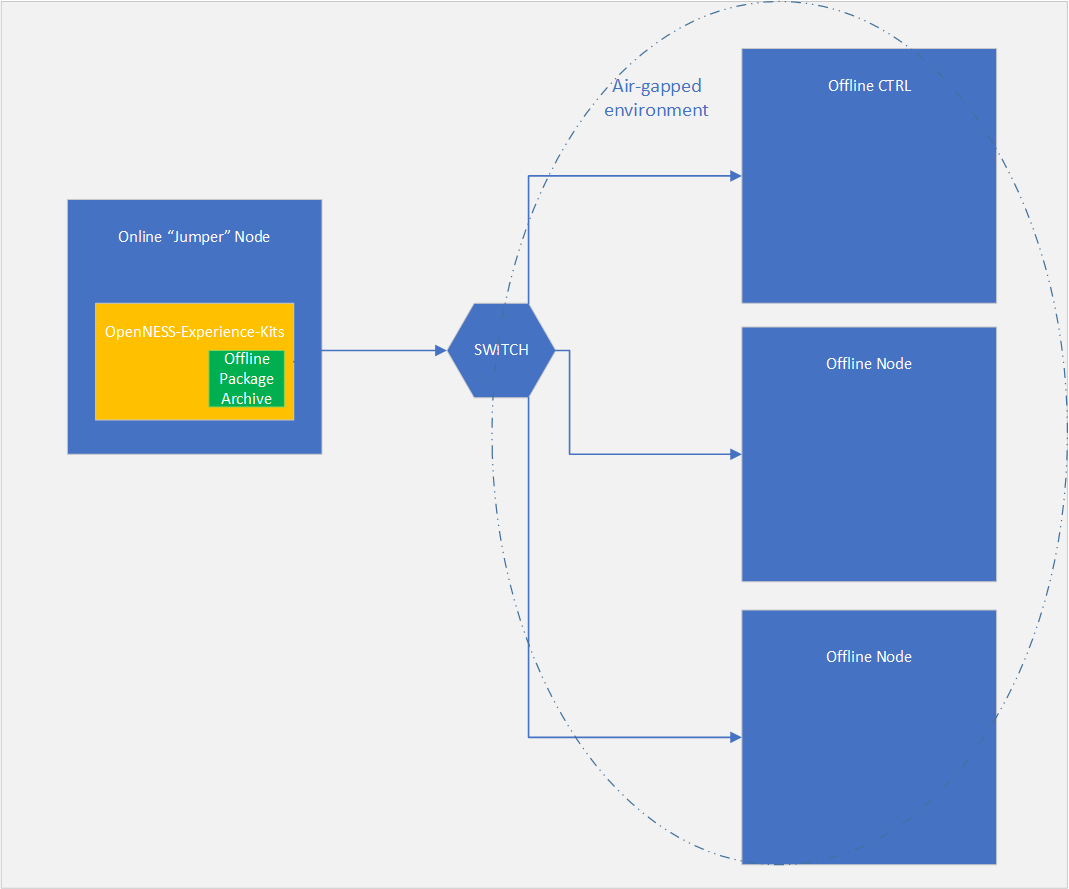 Figure 2. Scenario two - CEEK copied to the air-gapped network
Figure 2. Scenario two - CEEK copied to the air-gapped network
Setup prerequisites
- A node with access to internet to create the offline package.
- Cluster set up in an air-gapped environment.
- Clean setup, see pre-requisites
- [Optional] If CEEK is run from an online jumper node, the node needs to be able to SSH into each machine in air-gapped environment.
- [Optional] A media such as USB drive to copy the offline CEEK package to the air-gapped environment if there is no connection from online node.
- All the nodes in air-gapped environment must be able to SSH to each other without requiring password input, see getting-started.md.
- The control plane node needs to be able to SSH itself.
- The time and date of the nodes in offline environment is manually synchronized by the cluster’s admin.
- User provided files - OPAE_SDK_1.3.7-5_el7.zip and syscfg_package.zip.
- User provided files - ice-1.3.2.tar.gz and iavf-4.0.2.tar.gz when
e810_driver_enableflag is set (default setting).
Creating the offline package from an online node
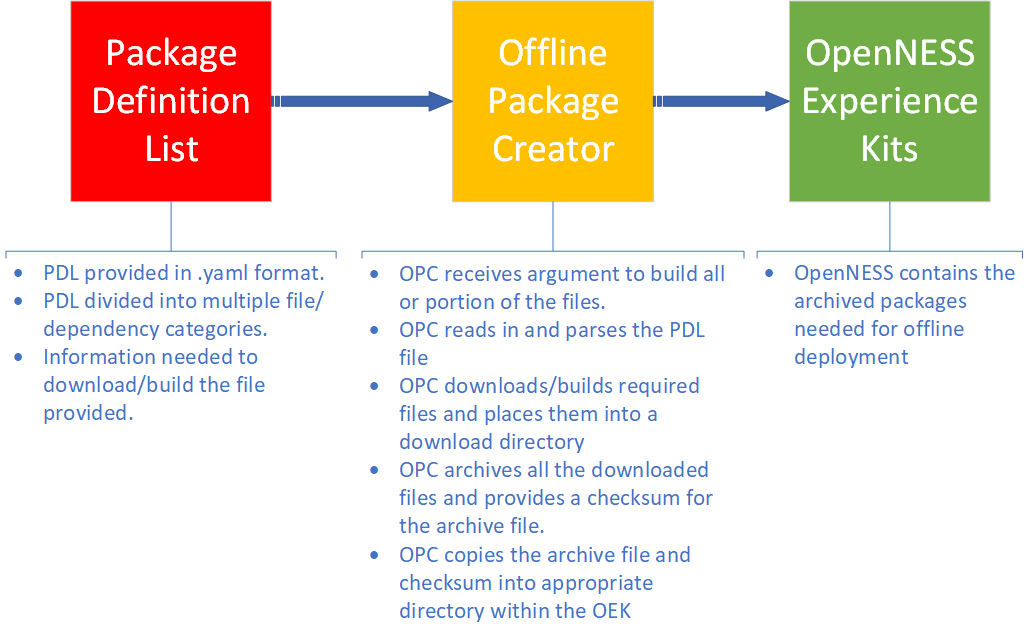
To create the offline package the user must have an access to an online node from which the offline package creator can download all necessary files and build Docker images. The list of files to be downloaded/build is provided in a form of a package definition list (Only package definition list for “flexran” flavor of Smart Edge Open is provided at the time of writing). Various categories of files to be downloaded are provided within this list including: RPMs, PIP pacakges, Helm charts, Dockerfiles, Go modules, and miscellaneous downloads. According to the category of a file the logic of offline package creator script will handle the download/build accordingly. Some files such as proprietary packages need to be provided by user in specified directories (see following steps). Once the offline package creator collects all necessary components it will pack them into an archive and then place them in appropriate place within the Converged Edge Experience Kits directory. Once the packages are archived the Converged Edge Experience Kits are ready to be deployed in air-gapped environment. The following diagram illustrates the workflow of the offline package creator. Additional information regarding the offline package creator can be found in the README.md file.
Figure 3. Offline package creator workflow
To run the offline package creator, follow the steps as below:
NOTE: RT components will require installation of RT kernel on the node by the OPC
Clone the Converged Edge Experience Kits repo to an online node:
# https://github.com/smart-edge-open/ido-converged-edge-experience-kits.git
Navigate to offline package creator directory:
# cd ido-converged-edge-experience-kits/offline_package_creator/
Create a directory from which user provided files can be accessed:
# mkdir /<usr>/<provided>/<directory>
Copy the ‘OPAE_SDK_1.3.7-5_el7.zip’ file (optional but necessary by default - to be done when OPAE is enabled in “flexran” flavor of CEEK) and syscfg_package.zip (optional but necessary by default- to be done when BIOS config is enabled in “flexran” flavor of CEEK) to the provided directory:
# cp OPAE_SDK_1.3.7-5_el7.zip /<usr>/<provided>/<directory>
# cp syscfg_package.zip /<usr>/<provided>/<directory>
Create the ido-converged-edge-experience-kits/ceek/nic_drivers directory and copy the ice-1.3.2.tar.gz and iavf-4.0.2.tar.gz files (optional but necessary by default - to be done when e810_driver_enable is enabled in “flexran” flavor of CEEK) to the directory.
# mkdir ./ceek/nic_drivers
# cp ice-1.3.2.tar.gz ./ceek/nic_drivers
# cp iavf-4.0.2.tar.gz ./ceek/nic_drivers
Edit ido-converged-edge-experience-kits/offline_package_creator/scripts/initrc file and update with GitHub username/token if necessary, HTTP/GIT proxy if behind firewall and provide paths to file dependencies.
# smart-edge-open token
GITHUB_TOKEN=""
# User add ones
GIT_PROXY="http://<address>:<port>"
# location of OPAE_SDK_1.3.7-5_el7.zip
BUILD_OPAE=disable
DIR_OF_OPAE_ZIP="/<usr>/<provided>/<directory>"
# location of syscfg_package.zip
BUILD_BIOSFW=disable
DIR_OF_BIOSFW_ZIP="/<usr>/<provided>/<directory>"
# location of the zip packages for collectd-fpga
BUILD_COLLECTD_FPGA=disable
DIR_OF_FPGA_ZIP="/<usr>/<provided>/<directory>"
Start the offline package creator script ido-converged-edge-experience-kits/offline_package_creator/offline_package_creator.sh
# bash offline_package_creator.sh all
The script will download all the files define in the pdl_flexran.yml and build other necessary images, then copy them to a designated directory. Once the script is finished executing the user should expect three files under the ido-converged-edge-experience-kits/roles/offline_roles/unpack_offline_package/files directory:
# ls ido-converged-edge-experience-kits/roles/offline_roles/unpack_offline_package/files
checksum.txt prepackages.tar.gz opcdownloads.tar.gz
Once the archive packages are created and placed in the CEEK, the CEEK is ready to be configured for offline/air-gapped installation.
Placing the complete offline package in offline environment
User has two options of deploying the CEEK for offline/air-gapped environment. Please refer to Figure 1 and Figure 2 of this document for diagrams.
Scenario 1: User will deploy the CEEK from an online node with a network connection to the offline/air-gapped environment. In this case if the online node is the same one as the one on which the offline package creator was run and created the archive files for CEEK than the CEEK directory does not need to be moved and will be used as is. The online node is expected to have a password-less SSH connection with all the offline nodes enabled - all the offline nodes are expected to have a password-less SSH connection between control plane and node and vice-versa, and the control plane node needs to be able to SSH itself.
Scenario 2: User will deploy the CEEK from a node within the offline/air-gapped environment. In this case the user needs to copy the whole CEEK directory containing the archived files from previous section from the online node to one of the nodes in the offline environment via USB drive or alternative media. It is advisable that the offline node used to run the CEEK is a separate node to the actual cluster, if the node is also used as part of the cluster it will reboot during the script run due to kernel upgrade and the CEEK will need to be run again - this may have un-forseen consequences. All the offline nodes are expected to have a password-less SSH connection between control plane and node and vice-versa, and the control plane node needs to be able to SSH itself.
Regardless of the scenario in which the CEEK will be deployed the deployment method is the same.
Deployment in offline environment
Once all the previous steps provided within this document are completed and the CEEK with offline archives is placed on the node which will run the CEEK automation, the user should get familiar with the “Running-playbooks” and “Preconditions” sections of getting started guide and deploy the Smart Edge Open as per usual deployment steps. Please note only deployment of “flexran” flavour is supported for offline/air-gapped environment, other flavours/configurations and default deployment may fail due to missing dependencies, the support for ACC100 accelerator is not available for offline deployment of “flexran” flavour at the time of writing. Both multi-node and single node modes are supported.
During the deployment of the offline version of the CEEK the archived files created by the offline package creator will be extracted and placed in appropriate directory. The CEEK will set up a local file share server on the control plane node and move the files to the said server. The CEEK will also create a local yum repo. All the files and packages will be pulled from this file share server by nodes across the air-gapped Smart Edge Open cluster. During the execution of the CEEK the Ansible scripts will follow the same logic as per the online mode with the difference that all the components will be pulled locally from the file share server instead of the internet.
The following are the specific steps to enable offline/air-gaped deployment from CEEK:
Enable the offline deployment in ido-converged-edge-experience-kits/inventory/default/group_vars/all/10-open.yml
## Offline Mode support
offline_enable: True
Make sure the time on offline nodes is synchronized.
Make sure nodes can access each other through SSH without password. Make sure cotrol-plane node can SSH itself. ie:
# hostname -I | awk '{print $1}'
<local IP>
# ssh-copy-id root@<local IP>
If a non-root user is being used (ie. openness) to deploy the cluster, a rule needs to be added, allowing the controller node to access itself through SSH without password.
# hostname -I | awk '{print $1}'
<local IP>
# ssh-copy-id root@<local IP>
$ ssh-copy-id openness@<local IP>
Make sure the CPUs allocation in “flexran” flavor is configured as desired, see configs in flavor directory.
Deploy Smart Edge Open using FlexRAN flavor for multi or single node:
- Update the
inventory.yamlfile by setting the deployment flavor asflexranand set single node deployment flag totruefor single node deployment:--- all: vars: cluster_name: offline_flexran_cluster flavor: flexran single_node_deployment: false # set true for single node ...NOTE: set
single_node_deployment:totruefor single node - Install the pre-requisites.
# ./scripts/ansible-precheck.sh - Run deployment:
# python3 deploy.pyNOTE: for more details about deployment and defining inventory please refer to CEEK getting started page.