SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
Copyright (c) 2019-2021 Intel Corporation
Smart Edge Open Integration with Baidu OpenEdge
Overview
Smart Edge Open is an open-source software toolkit to enable easy orchestration and management of edge services across diverse network platforms and access technologies in multi-cloud environments. Smart Edge Open can integrate with Baidu* Cloud Connector, OpenEdge, which is Edge IoT Gateway. Together with Baidu edge management dashboard, the whole Baidu Edge solution is called Baidu IntelliEdge*. For more details, refer to Baidu’s website: www.baidu.com
This application note provides guidelines and examples on:
- Integration architecture description
- Run Baidu OpenEdge on the Smart Edge Open platform
- End-to-end example
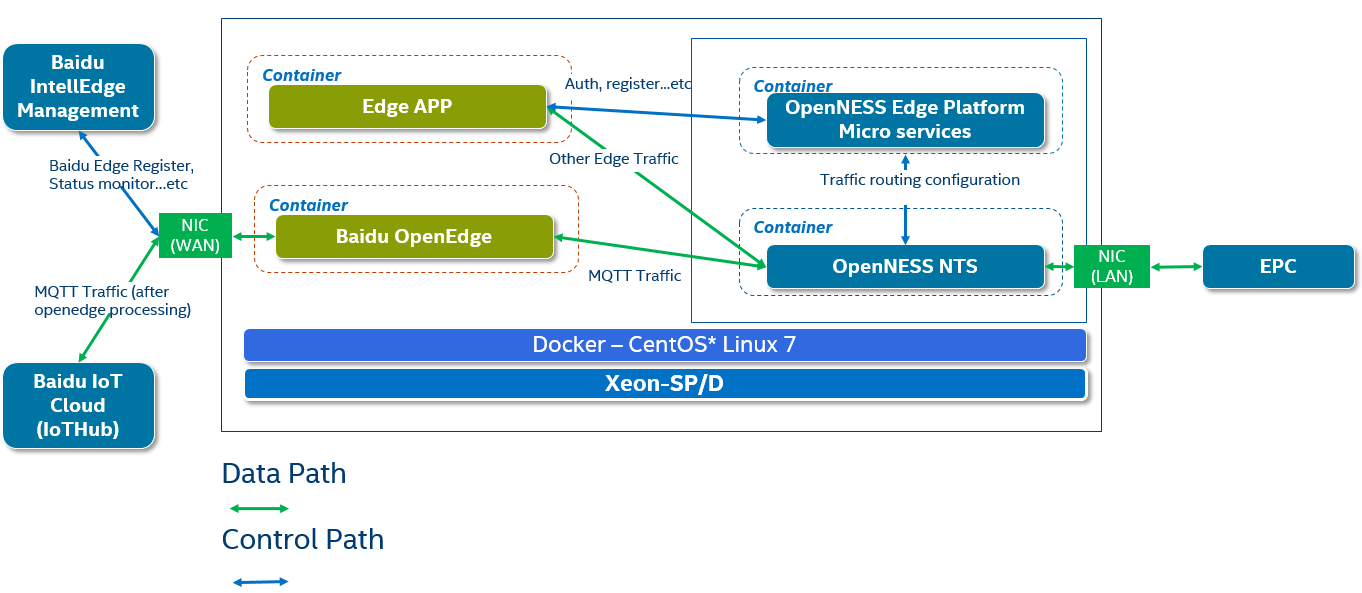
Integration Architecture
Figure 1. Integration Architecture for OpenEdge on Smart Edge Open
«««< HEAD
 =======
=======

b04e08260bf4c44b1c204d578b22db1366c1793d
-
Smart Edge Open Edge platform supports cloud-native infrastructure. Baidu OpenEdge and other edge apps can run as a separate container. Smart Edge Open NTS will send/receive data traffic to/from the apps according to traffic routing configuration.
-
OpenEdge can play as two types of Apps
- Producer: provides a service to other apps on the Edge Platform (need a control path between OpenEdge and Smart Edge Open for EAA interaction).
- Consumer: consumes end-user traffic and optionally can get services from producer apps on the same edge platform. If the Consumer needs to get services from other edge apps, they need to use a control path to authenticate and register with Smart Edge Open.
NOTE: In the application note, OpenEdge is treated as a pure consumer application and does not need to get service from other edge apps. Thus, in the integration architecture diagram, there is no control path.
Run OpenEdge on Smart Edge Open
This section describes how to set up and run OpenEdge as a consumer application on Smart Edge Open based on cloud-native infrastructure.
Smart Edge Open Setup
Follow the Smart Edge Open user guide to prepare a setup environment, deploy Smart Edge Open, and configure traffic routing rules.
OpenEdge Setup
Scripts overview
In the Smart Edge Open release package, it provides example scripts to help users with the setup.
The scripts are located in the release package with the folder name setup_baidu_openedge as shown in the structure below:
setup_baidu_openedge
├── 01_setup.sh
├── 02_build.sh
├── 03_deploy.sh
├── composefile
│ ├── democfg
│ ├── docker-compose.yml
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ └── entrypoint.sh
├── docker
│ ├── cleanup.yml
│ ├── compose_build.yml
│ └── compose_up.yml
├── mqtt
│ ├── devices
│ │ ├── openedge_pub.py
│ │ └── openedge_sub.py
│ └── rtt
│ ├── measure_rtt_iothub.py
│ └── measure_rtt_openedge.py
├── tasks
│ ├── build_main.yml
│ ├── deploy_main.yml
│ ├── script_success.yml
│ └── setup_main.yml
└── vars
└── defaults.yml
There are three main scripts: 01_setup.sh, 02_build.sh, and 03_deploy.sh. The scripts need to be executed as the root user in the order
from the local console on the Smart Edge Open server or remotely via SSH. The other scripts will be called by the three main scripts for the setup.
- The folder -
mqttcontains MQTT IOT device simulators for end-to-end testing so that they should be executed from device machines. - The folder -
democfgis where you should put files downloaded from the Baidu* cloud to bring up OpenEdge. For details, refer to the below chapter. - To run the scripts correctly, make sure that the folder
setup_baidu_openedgeis located at :appliance-ce/scripts/ansible/examples/
Prepare OpenEdge certs and configuration files
Before you build and run OpenEdge, sign up for a Baidu* account to get certification and configuration files necessary for OpenEdge. gateway to register with Baidu IntelliEdge* management suite, which provides a management dashboard for managing OpenEdge gateway. For details on how to get those Baidu’s files, go to: https://cloud.baidu.com/ and search the following keyword: Baidu IntelliEdge.
In the folder: setup_baidu_openedge/composefile/democfg, put the certification and configuration files from Baidu IntelliEdge into the folder.
When building a container image for OpenEdge, those files will be copied into the image. The sub-directory structure in the democfg should look like the following:
├── democfg
│ ├── agent-cert
│ │ ├── client.key
│ │ ├── client.pem
│ │ ├── openapi.pem
│ │ └── root.pem
│ ├── agent-conf
│ │ └── service.yml
│ ├── application.yml
│ └── remote-iothub-conf
│ └── service.yml
The following code describes an example configuration for your reference, and the example configurations can be used for the end-to-end example demo in chapter 4.0 End to End Example Demo. Democfg/application.yml example:
version: v0
services:
- name: localhub
image: openedge-hub
replica: 1
mounts:
- name: localhub-conf
path: etc/openedge
readonly: true
- name: localhub-cert
path: var/db/openedge/cert
readonly: true
- name: localhub-data
path: var/db/openedge/data
- name: localhub-log
path: var/log/openedge
# native process mode only
- name: openedge-hub-bin
path: lib/openedge/openedge-hub
readonly: true
- name: agent
image: openedge-agent
replica: 1
mounts:
- name: agent-conf
path: etc/openedge
readonly: true
- name: agent-cert
path: var/db/openedge/cert
readonly: true
- name: agent-volumes
path: var/db/openedge/volumes
- name: agent-log
path: var/log/openedge
# native process mode only
- name: openedge-agent-bin
path: lib/openedge/openedge-agent
readonly: true
- name: remote-iothub
image: openedge-remote-mqtt
replica: 1
mounts:
- name: remote-iothub-conf
path: etc/openedge
readonly: true
- name: remote-iothub-cert
path: var/db/openedge/cert
readonly: true
- name: remote-iothub-log
path: var/log/openedge
# native process mode only
- name: openedge-remote-mqtt-bin
path: lib/openedge/openedge-remote-mqtt
readonly: true
volumes:
# hub
- name: localhub-conf
path: var/db/openedge/localhub-conf
- name: localhub-data
path: var/db/openedge/localhub-data
- name: localhub-cert
path: var/db/openedge/localhub-cert-only-for-test
- name: localhub-log
path: var/db/openedge/localhub-log
# agent
- name: agent-conf
path: var/db/openedge/agent-conf
- name: agent-cert
path: var/db/openedge/agent-cert
- name: agent-volumes
path: var/db/openedge
- name: agent-log
path: var/db/openedge/agent-log
# remote mqtt
- name: remote-iothub-conf
path: var/db/openedge/remote-iothub-conf
- name: remote-iothub-cert
path: var/db/openedge/remote-iothub-cert
- name: remote-iothub-log
path: var/db/openedge/remote-iothub-log
# bin, native process mode only
- name: openedge-hub-bin
path: var/db/openedge/openedge-hub
- name: openedge-agent-bin
path: var/db/openedge/openedge-agent
- name: openedge-remote-mqtt-bin
path: var/db/openedge/openedge-remote-mqtt
Democfg/ agent-cert/ example:
The cert files should be downloaded from the Baidu IntelliEdge management dashboard for the OpenEdge gateway and put into the following subfolder: /democfg/agent-cert/.
Democfg/ agent-conf/service.yml example:
The service.yml file should be downloaded from the Baidu IntelliEdge management dashboard for the OpenEdge gateway and put into the following subfolder: /democfg/agent-conf/.
Democfg/remote-iothub-conf/service.yml example:
hub:
address: tcp://0.0.0.0:1883
username: test
password: hahaha
remotes:
- name: remotemec
address: 'tcp://xxxx.mqtt.iot.gz.baidubce.com:1883\'
clientid: xxxxxx
username: xxxx/xxxx
password: xxxxxxxxxxxx
rules:
- hub:
subscriptions:
- topic: t/topic
remote:
name: remotemec
subscriptions:
- topic: rtt
qos: 1
logger:
path: var/log/openedge/service.log
level: "debug"
The configuration file is used for testing the IoT data route from Baidu OpenEdge to IoTHub Cloud (also named as IoTHub). To get more information about Baidu IotHub Cloud, go to cloud.baidu.com, and search for the following keyword: iothub.
Running scripts – build and run OpenEdge
On the server that is running Smart Edge Open, execute the scripts as shown below:
01_setup.sh
02_build.sh
03_deploy.sh
After competition for each script, the expected successful print should be:
"msg": "Script completed successfully"
Check the Docker information to make sure that the container STATUS is Up.
#docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
f83a63f3f11e composefile_baidu_edge "entrypoint.sh" 4 seconds ago
Up 3 seconds 0.0.0.0:443->443/tcp, 0.0.0.0:1883-1884->1883-1884/tcp
composefile_baidu_edge_1
End to End Example Demo
Overview
Figure 2. End to End Example Diagram.
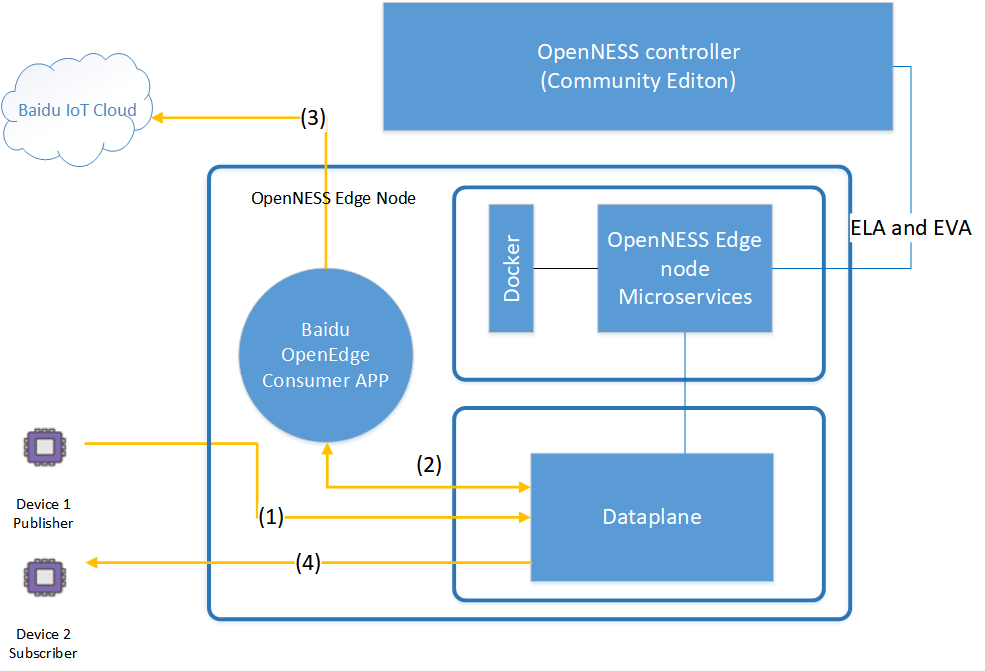
This is an end-to-end example demo for MQTT traffic. This could be an IoT industrial application. It consists of the following elements and related IoT data processing:
-
Two MQTT devices as publisher and subscriber. The MQTT client software is used to simuate two MQTT IoT devices.
- Smart Edge Open Controller: performs management and policy configuration. For this example, the controller will configure traffic rules for routing MQTT IOT traffic to Baidu OpenEdge via Smart Edge Open.
- Baidu OpenEdge: In the example provided, the Smart Edge Open Baidu OpenEdge app is deployed as a pure Consumer app which does not consume any services from producer applications on the edge node. Hence, the Baidu OpenEdge app does not need to call EAA APIs. The app will handle data traffic from/to MQTT devices via the Smart Edge Open dataplane.
NOTE: Implementing EAA APIs in the Baidu OpenEdge application will further enhance the capability of the Baidu OpenEdge based application as they can consume services, such as location and radio network information, from the Edge Node.
- IOT MQTT Data plane processing: (1) Device #1 publishes its status data by using the MQTT protocol. (2) The Smart Edge Open Platform forwards the traffic to Baidu OpenEdge according to traffic rules. Baidu OpenEdge will then perform local computing and data filtering. (3) According to the topic configuration, Baidu OpenEdge sends data to Baidu Cloud. (4) Also, Baidu OpenEdge forwards the message to device #2 subscriber.
Run MQTT simulator
The Smart Edge Open release package provides example scripts to help users run the MQTT simulator and RTT testing.
The scripts can be found in the release package with the subfolder name setup_baidu_openedge/mqtt as the below structure:
├── devices
│ ├── openedge_pub.py
│ └── openedge_sub.py
└── rtt
├── measure_rtt_iothub.py
└── measure_rtt_openedge.py
Before running the scripts, install python3.6 and paho mqtt on a CentOS* Linux* machine, where the recommended version is CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core). The following are recommended install commands:
sudo yum -y install epel-release
sudo yum update
sudo yum install python36
sudo yum install python36-pip
sudo pip3 install paho-mqtt
Test OpenEdge Sub and Pub:
Data path is:
Device#1 publisher -> Smart Edge Open -> OpenEdge -> Smart Edge Open -> Deivce#2 Subscriber.
Run commands separately on each device machine:
python3.6 openedge_pub.py -e [openedge_address] -c clientA -u test -s hahaha -t t
python3.6 openedge_sub.py -e [openedge_address] -c clientB -u test -s hahaha -t t/topic
NOTE: [openedge_address] is ip address of OpenEdge gateway.
Expected result on the subscriber:
Received Message of Topic t/topic
Message Content: b\'{\"wmId\": 0,\"aa\": b,\"cc\": {\"p\": 99,\"kk\":x}}\'
Test OpenEdge Route to IotHub:
The data path is:
Device#1 publisher -> Smart Edge Open -> OpenEdge -> IoTHub -> Deivce#2 Subscriber.
Run commands separately on each device machine:
python3.6 openedge_sub.py -e [iothub_address] -c clientA -u [iothub_username] -s [iothub_password] -t t/topic
python3.6 openedge_pub.py -e [openedge_address] -c clientB -u test -s hahaha -t t
NOTE: The iothub_address, iothub_username, and iothub_password will be assigned when registering user for Baidu IoTHub.
Expected result on the subscriber:
Received Message of Topic t/topic
Message Content: b\'{\"wmId\": 0,\"aa\": b,\"cc\": {\"p\": 99,\"kk\":x}}\'
RTT Test with OpenEdge:
The data path is:
Device#1 publisher -> Smart Edge Open -> OpenEdge -> Smart Edge Open -> Deivce#1 Subscriber.
Run the following command on first device machine (here, the device will play as publisher and subscriber):
python3.6 measure_rtt_openedge.py -e [openedge_address] -c clientRTT -u test -s hahaha -t t -b t/topic
NOTE: [openedge_address] is an IP address of OpenEdge gateway.
Expected result on the subscriber:
===receve message from topic: t/topic
avg delay (ms) = 1.7480066461309578
And the output statistics file is: rtt\_openedge.csv
RTT Test with IoTHub:
The data path is:
Device#1 publisher -> Smart Edge Open -> OpenEdge -> IoTHub -> Deivce#1 Subscriber.
Run the following command on first device machine (here, the device will play as publisher and subscriber):
python3.6 measure_rtt_iothub.py -e [iothub_address] -c clientA -u [iothub_username] -s [iothub_password] -t rtt -b rtt
NOTE: [iothub_address] is the IP address of Baidu IotHub. rtt is a topic that is pre-configured on iotHub.
The expected result on the subscriber:
===receve message from topic: t/topic
avg delay (ms) = 1.7480066461309578
And the output statistics file is: rtt\_iothub.csv