SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
Copyright (c) 2019-2020 Intel Corporation
Core Network Configuration Agent (CNCA)
- 4G/LTE Core Configuration using CNCA
- 5G NGC components bring up and Configuration using CNCA
- Network Edge mode
- Bring up of NGC components in Network Edge mode
- Configuring in Network Edge mode
- Traffic Influence Subscription description
- Packet Flow Description transaction description
- Policy Authorization Application Session Context description
- Network Edge mode
4G/LTE Core Configuration using CNCA
Configuring in Network Edge mode
For Network Edge mode, CNCA provides a kubectl plugin to configure the 4G/LTE Core network. Kubernetes* adopts plugins concepts to extend its functionality. The kube-cnca plugin executes CNCA related functions within the Kubernetes eco-system. The plugin performs remote callouts against LTE Control and User Plane Separation (LTE CUPS) Operation Administration and Maintenance (OAM) agent.
Available management with kube-cnca against LTE CUPS OAM agent are:
- Creation of LTE CUPS userplanes
- Deletion of LTE CUPS userplanes
- Updating (patching) LTE CUPS userplanes
The kube-cnca plugin is installed automatically on the control plane during the installation phase of the Converged Edge Experience Kits.
In the following sections, a detailed explanation with examples is provided about the CNCA management.
Creation of the LTE CUPS userplane is performed based on the configuration provided by the given YAML file. The YAML configuration should follow the provided sample YAML in Sample YAML LTE CUPS userplane configuration section. Use the apply command to post a userplane creation request onto Application Function (AF):
kubectl cnca apply -f <config.yml>
When the userplane is created successfully, the apply command returns the userplane identifier <userplane-id>, which should be used in further correspondence with LTE CUPS OAM agent concerning this particular userplane. It is the responsibility of the user to retain the <userplane-id> as kube-cnca is a stateless function.
NOTE: All active userplanes can be retrieved from AF through the command
kubectl cnca get userplanes.
To retrieve an existing userplane with a known userplane ID, use the following command:
kubectl cnca get userplane <userplane-id>
To retrieve all active userplanes at LTE CUPS OAM agent, use the following command:
kubectl cnca get userplanes
To modify an active userplane, use the patch command and provide a YAML file with the subset of the configuration to be modified:
kubectl cnca patch <userplane-id> -f <config.yml>
To delete an active userplane, use the delete command:
kubectl cnca delete userplane <userplane-id>
Sample YAML LTE CUPS userplane configuration
Similarly, the kube-cnca expects the YAML configuration for the LTE CUPS-specific information as shown in the following format. The file must contain the topmost configurations: apiVersion, kind, and policy.
apiVersion: v1
kind: lte
policy:
id: '5'
uuid: beauty
function: SAEGWU
config:
s5u_pgw:
up_ip_address: 192.168.120.122
s1u:
up_ip_address: 192.190.120.122
s5u_sgw:
up_ip_address: 192.168.120.122
selectors:
- id: select001
network:
mcc: '466'
mnc: '92'
uli:
tai:
tac: 51
pdn:
apns:
- APN001
5G NGC components bring up and Configuration using CNCA
Smart Edge Open provides Ansible* scripts for setting up NGC components for two scenarios. Each of the scenarios is supported by a separate role in the Converged Edge Experience Kits:
Role “ngc” This role brings up the 5g Smart Edge Open setup in the loopback mode for testing and demonstrating its usability. The Ansible scripts that are part of the “ngc” role build, configure, and start AF, Network Exposure Function (NEF), OAM, and Core Network Test Function (CNTF) in the Network Edge mode. Within this role, AF and OAM are set up on the controller node. NEF and CNTF are set up on the edge node. The description of the configuration and setup of the NGC components provided in the next sections of this document refers to the ngc role. The NGC components set up within the ngc role can be fully integrated and tested with the provided kubectl plugin or CNCA UI.
Network Edge mode
Bring up of NGC components in Network Edge mode
-
If Smart Edge Open (Edge Controller + Edge Node) is not yet deployed through converged-edge-experience-kits, then: Set
flavorascore-cplaneininventory.yml(a sampleinventory.ymlis shown as below) before runningdeploy.pyas described in Smart Edge Open Network Edge: Controller and Edge node setup document. If not, skip this step.--- all: vars: cluster_name: cluster_test # NOTE: Use `_` instead of spaces. flavor: core-cplane # NOTE: Flavors can be found in `flavors` directory. single_node_deployment: true # Request single node deployment (true/false). limit: # Limit ansible deployment to certain inventory group or hosts controller_group: hosts: controller: ansible_host: 172.16.0.1 ansible_user: openness edgenode_group: hosts: node01: ansible_host: 172.16.0.1 ansible_user: openness -
If Smart Edge Open Edge Controller + Edge Node is already deployed (but without enabling the ngc role) and at a later stage you want to enable NGC components then: Enable the role for ngc by changing the
ne_ngc_enablevariable totrueininventory/default/group_vars/all/20-enhanced.ymland then re-rundeploy.pywith specifiedlimit: controllervariable ininventory.yml(define only one cluster on which the role should be enabled) as described in Smart Edge Open Network Edge: Controller and Edge node setup document.NOTE: In addition to the Smart Edge Open controller bring up, by enabling the ngc role, the playbook scripts performs:
- A clone of the ido-epcforedge repo from GitHub*
- Builds AF, NEF, OAM, and CNTF microservices
- Generates certificate files at the location /opt/openness/certs/ngc on the controller.
- Creates ConfigMap certs-cm from the above directory.
- Updates the configuration files of AF and NEF with the service names of NEF and CNTF respectively.
- Copies the OAM, NEF, CNTF and AF configuration to the location /opt/openness/configs/ngc on the controller.
- Creates ConfigMap oauth2-cm from the /opt/openness/configs/ngc/oauth2.json configuration file.
- Creates template of ConfigMaps af-cm,nef-cm,cntf-cm,oam-cm from the respective configuration json files present in the /opt/openness/configs/ngc directory.
- Copies these templates to the respective template folders of the helm charts for AF, NEF, OAM, and CNTF.
- Creates docker images for AF, NEF, OAM, and CNTF microservices and adds them into the Docker* registry at <controller ip:port>.
- Installs the helm charts for AF, NEF, OAM, and CNTF using the images from the Docker registry
- Copies the helm charts for AF, NEF, OAM, and CNTF into the location /opt/openness/helm-charts/
-
On successful AF, NEF, OAM, and CNTF PODs should start. Status of PODs, Deployments, ConfigMaps, Services, images, and helm charts can be verified using the following commands:
- kubectl get pods -n ngc NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/af-6f5fb6c58f-bhgmk 1/1 Running 0 3d17h pod/cntf-d54ffd544-7xd8j 1/1 Running 0 3d17h pod/nef-55869fc678-wstfw 1/1 Running 0 3d17h pod/oam-659b5db5b5-cf7ds 1/1 Running 0 3d17h - kubectl get deployments -n ngc NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE af 1/1 1 1 3d17h cntf 1/1 1 1 3d17h nef 1/1 1 1 3d17h oam 1/1 1 1 3d17h - kubectl get cm -n ngc NAME DATA AGE af-cm 1 3d17h certs-cm 8 3d17h cntf-cm 1 3d17h nef-cm 1 3d17h oam-cm 1 3d17h oauth2-cm 1 3d17h - kubectl get services -n ngc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE afservice NodePort 10.100.106.19 <none> 8050:30050/TCP,8051:32475/TCP,30052:30052/TCP 3d17h cntfservice NodePort 10.98.244.147 <none> 8095:32178/TCP 3d17h nefservice NodePort 10.101.91.226 <none> 8060:30372/TCP 3d17h oamservice NodePort 10.97.33.7 <none> 8070:30070/TCP 3d17h - docker image ls REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE 10.190.212.218:5000/af-image 1.0 5f84239da40d 3 days ago 264MB 10.190.212.218:5000/oam-image 1.0 7e7220f7537d 3 days ago 261MB 10.190.212.218:5000/cntf-image 1.0 14ba6e5a9f27 3 days ago 261MB 10.190.212.218:5000/nef-image 1.0 b1cdae311319 3 days ago 263MB - helm list NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION af default 1 2020-07-20 18:02:31.158137849 +0530 IST deployed af-0.1.0 0.1.0 cntf default 1 2020-07-20 18:02:57.891084883 +0530 IST deployed cntf-0.1.0 0.1.0 nef default 1 2020-07-20 18:01:24.728140657 +0530 IST deployed nef-0.1.0 0.1.0 oam default 1 2020-07-20 18:00:06.184551692 +0530 IST deployed oam-0.1.0 0.1.0
Deploying the Network Edge Mode to work with 5G Core Network
The Smart Edge Open ngc role deploys the PODS as described below:
- AF and OAM PODs on the controller
- NEF and CNTF PODs on the node, where CNTF is a simulation of the core network functions used by NEF and AF.
If the AF configuration needs to be updated (as per your deployment configuration) to use the NEF from the 5G Core Network then complete the following steps:
-
Delete the NEF and CNTF PODs using helm:
helm uninstall nef release "nef" uninstalled helm uninstall cntf release "cntf" uninstalled -
Update the AF POD using helm:
- Open the AF configmap template file
/opt/openness/helm-charts/af/templates/configmapAF.yamland modify the parameters. - Save and exit.
- Now update the AF POD using the following command:
helm upgrade af /opt/openness/helm-charts/af --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/af-image Release "af" has been upgraded. Happy Helming! NAME: af LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 24 12:29:44 2020 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: deployed REVISION: 2 TEST SUITE: None NOTES: Chart af was successfully installed af image was saved in the docker registry Image name: <controller-ip>:5000/af-image:1.0 Your release is named af. To learn more about the release, try: $ helm status af $ helm get all af kubectl get pods -n ngc NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE af-7695ccb494-7v4zx 1/1 Running 0 2m39s oam-659b5db5b5-cf7ds 1/1 Running 0 3d18h- A successful restart of AF with the updated config can be observed through AF container logs. Run the following command to get AF logs:
kubectl logs -f af-7695ccb494-7v4zx --namespace=ngcSample output of the AF container logs with the updated config may appear as: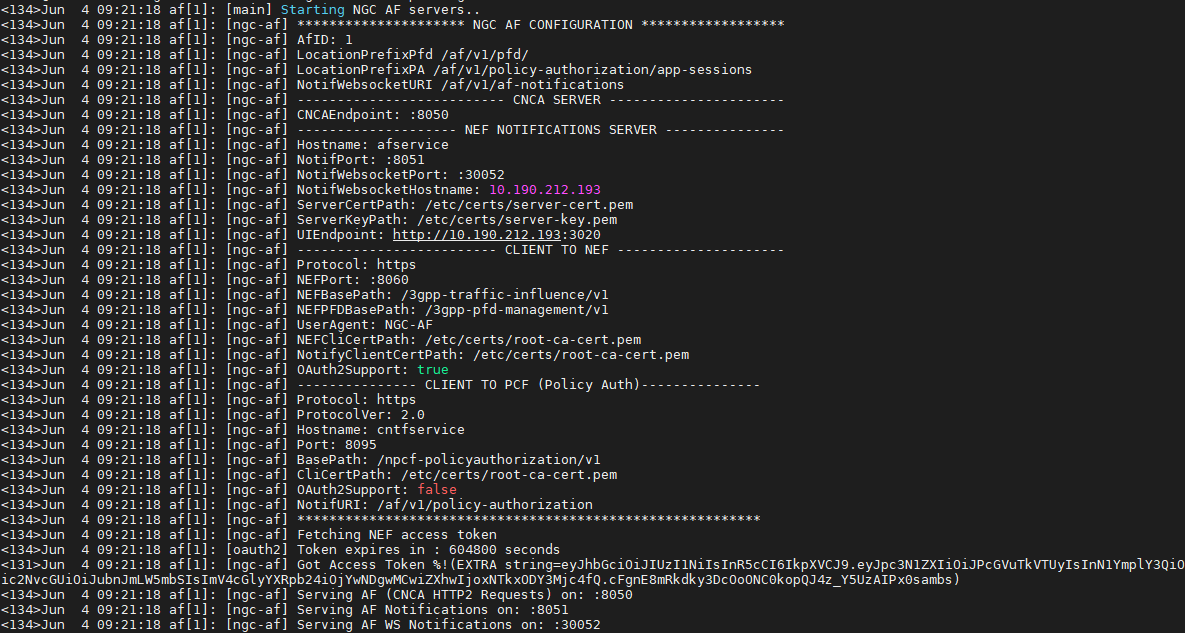
- Open the AF configmap template file
If the NEF configuration needs to be updated (as per your deployment configuration) to use the SMF/PCF/UDR from the 5G Core Network instead of CNTF, then complete the following steps:
-
Delete the CNTF PODs using helm:
helm uninstall cntf release "cntf" uninstalled -
Update the NEF POD using helm:
- Open the NEF configmap template file
/opt/openness/helm-charts/nef/templates/configmapNEF.yamland modify the parameters. - Save and exit.
- Now update the NEF POD using the following command:
helm upgrade nef /opt/openness/helm-charts/nef --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/nef-image Release "nef" has been upgraded. Happy Helming! NAME: nef LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Jul 24 12:37:20 2020 NAMESPACE: default STATUS: deployed REVISION: 2 TEST SUITE: None NOTES: Chart nef was successfully installed nef image was saved in the docker registry Image name: <controller-ip>:5000/nef-image:1.0 Your release is named nef. To learn more about the release, try: $ helm status nef $ helm get all nef kubectl get pods -n ngc NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE af-7695ccb494-7v4zx 1/1 Running 0 8m29s nef-77d67c6778-ph5t4 1/1 Running 0 45s oam-659b5db5b5-cf7ds 1/1 Running 0 3d18h - Open the NEF configmap template file
Modifying the OAM configuration. Follow the same steps as above (as done for AF) with the following differences:
- Open the file
/opt/openness/helm-charts/oam/templates/configmapOAM.yamland modify the parameters. - Save and exit.
- Now restart the OAM POD using the command:
helm upgrade oam /opt/openness/helm-charts/oam --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/oam-image
- A successful restart of the OAM with the updated config can be observed through OAM container logs. Run the following command to get OAM logs:
kubectl logs -f oam-659b5db5b5-l26q8 --namespace=ngc
Modifying the oauth2 configuration. Complete the following steps:
- Open the file
/opt/openness/configs/ngc/oauth2.jsonand modify the parameters. - Save and exit.
-
Delete the CNTF, AF, and NEF PODs using helm:
helm uninstall cntf release "cntf" uninstalled helm uninstall nef release "nef" uninstalled helm uninstall cntf release "af" uninstalled -
Update the ConfigMap associated with oauth2.json:
kubectl create configmap oauth2-cm --from-file /opt/openness/configs/ngc/oauth2.json -n ngc -o yaml --dry-run=client | kubectl replace -f - -
Restart NEF, CNTF, and AF PODs using the following commands:
helm install nef /opt/openness/helm-charts/nef --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/nef-image helm install af /opt/openness/helm-charts/af --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/af-image helm install cntf /opt/openness/helm-charts/cntf --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/cntf-image
Modifying the certificates. Complete the following steps:
- Update the certificates present in the directory
/opt/openness/certs/ngc/.
-
Delete the CNTF, AF, NEF, and OAM PODs using helm:
helm uninstall cntf release "cntf" uninstalled helm uninstall nef release "nef" uninstalled helm uninstall cntf release "af" uninstalled helm uninstall oam release "oam" uninstalled -
Update the ConfigMap associated with the certificates directory:
kubectl create configmap certs-cm --from-file /opt/openness/certs/ngc/ -n ngc -o yaml --dry-run=client | kubectl replace -f - -
Check certs-cm present in available ConfigMaps list:
kubectl get cm -n ngc -
Restart NEF, CNTF, AF, and OAM PODs using the following commands:
helm install nef /opt/openness/helm-charts/nef --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/nef-image helm install af /opt/openness/helm-charts/af --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/af-image helm install cntf /opt/openness/helm-charts/cntf --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/cntf-image helm install oam /opt/openness/helm-charts/oam --set image.repository=<controller-ip>:5000/oam-image
Configuring in Network Edge mode
For Network Edge mode, the CNCA provides a kubectl plugin to configure the 5G Core network. Kubernetes adopted plugin concepts to extend its functionality. The kube-cnca plugin executes CNCA related functions within the Kubernetes ecosystem. The plugin performs remote callouts against NGC OAM and AF microservice on the controller itself.
The kube-cnca plugin is installed automatically on the control plane node during the installation phase of the Converged Edge Experience Kits
Edge Node services operations with 5G Core (through OAM interface)
NOTE: Registration of the Smart Edge Open Controller’s AF instance with the 5G core must be performed manually (or through any other interface) exposed by the 5G Core. OAM capabilities will be enhanced in future releases to support this. The current version of OAM supports only one instance of the Smart Edge Open Controller to communicate.
Registration of UPF services associated with Edge-node with 5G Core
Supported operations through kube-cnca plugin:
- Registration of edge service info for UPF with a 5G Core through OAM interface (co-located with Edge-Node)
- Un-registration of edge service info
To register the AF service through the NGC OAM function, run:
kubectl cnca register --dnai=<DNAI> --dnn=<DNN> --tac=<TAC> --priDns=<pri-DNS> --secDns=<sec-DNS> --upfIp=<UPF-IP> --snssai=<SNSSAI>
The following parameters MUST be provided to the command:
- Data Network Access Identifier (DNAI)
- Data Network Name (DNN)
- Primary DNS (priDns)
- Secondary DNS (secDns)
- UPF IP Address (upfIp)
- Network Slice Identifier (SNSSAI)
Upon successful registration, subscriptions can be instantiated over the NGC AF. The af-service-id is returned by the register command to be used in further correspondence with NGC OAM and AF functions.
Un-registration of the AF service can be performed with the following command:
kubectl cnca unregister <af-service-id>
Traffic influence operations with 5G Core (through AF interface)
Supported operations through kube-cnca plugin:
- Creation of traffic influence subscriptions through the AF microservice to steer application traffic towards edge-node
- Deletion of subscriptions
- Updating (patching) subscriptions
- get or get-all subscriptions
Creation of the AF subscription is performed based on the configuration provided by the given YAML file. The YAML configuration should follow the provided sample YAML in the Sample YAML NGC AF subscription configuration section. Use the apply command to post a subscription creation request onto AF:
kubectl cnca apply -f <config.yml>
When the subscription is successfully created, the apply command will return the subscription URL that includes a subscription identifier at the end of the string. Only this subscription identifier <subscription-id> should be used in further correspondence with AF concerning this particular subscription. For example, https://localhost:8060/3gpp-traffic-influence/v1/1/subscriptions/11111 and subscription-id is 11111. It is the responsibility of the user to retain the <subscription-id> as kube-cnca is a stateless function.
To retrieve an existing subscription with a known subscription ID, use the following command:
kubectl cnca get subscription <subscription-id>
To retrieve all active subscriptions at AF, execute this command:
kubectl cnca get subscriptions
To modify an active subscription, use the patch command and provide a YAML file with the subset of the configuration to be modified:
kubectl cnca patch <subscription-id> -f <config.yml>
To delete an active subscription, use the delete command:
kubectl cnca delete subscription <subscription-id>
Sample YAML NGC AF subscription configuration
The kube-cnca expects the YAML configuration as in the format below. The file must contain the topmost configurations: apiVersion, kind, and policy. The configuration policy retains the NGC AF-specific subscription information.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ngc
policy:
afServiceId: 'afService001'
afAppId: 'afApp01'
afTransId: 'afTrans01'
appReloInd: false
dnn: 'edgeLocation001'
snssai:
sst: 0
sd: 'default'
gpsi: ''
ipv4Addr: '127.0.0.1'
ipv6Addr: ''
macAddr: ''
requestTestNotification: true
trafficRoutes:
- dnai: 'edgeLocation001'
routeInfo:
ipv4Addr: ''
ipv6Addr: ''
routeProfId: 'default'
Packet Flow Description operations with 5G Core (through AF interface)
Supported operations through the kube-cnca plugin:
- Creation of packet flow description (PFD) transactions through the AF microservice to perform accurate detection of application traffic for UPF in 5G Core
- Deletion of transactions and applications within a transaction
- Updating (patching) transactions and applications within a transaction
- Get or get all transactions.
- Get a specific application within a transaction
Creation of the AF PFD transaction is performed based on the configuration provided by the given YAML file. The YAML configuration should follow the provided sample YAML in the Sample YAML NGC AF transaction configuration section. Use the apply command as below to post a PFD transaction creation request onto AF:
kubectl cnca pfd apply -f <config.yml>
When the PFD transaction is successfully created, the apply command will return the transaction URL, which includes a transaction identifier at the end of the string. Only this transaction identifier <transaction-id> should be used in further correspondence with AF concerning this particular transaction. For example, https://localhost:8050/af/v1/pfd/transactions/10000 and transaction-id is 10000. It is the responsibility of the user to retain the <transaction-id> as kube-cnca is a stateless function.
To retrieve an existing PFD transaction with a known transaction ID, use the following command:
kubectl cnca pfd get transaction <transaction-id>
To retrieve all active PFD transactions at AF, run:
kubectl cnca pfd get transactions
To modify an active PFD transaction, use the patch command and provide a YAML file with the subset of the configuration to be modified:
kubectl cnca pfd patch transaction <transaction-id> -f <config.yml>
To delete an active PFD transaction, use the delete command:
kubectl cnca pfd delete transaction <transaction-id>
To retrieve an existing application within a PFD transaction with a known application ID and transaction ID, use:
kubectl cnca pfd get transaction <transaction-id> application <application-id>
To modify an application within an active PFD transaction, use the patch command and provide a YAML file with the subset of the configuration to be modified:
kubectl cnca pfd patch transaction <transaction-id> application <application-id> -f <config.yml>
To delete an application within an active PFD transaction, use the delete command:
kubectl cnca pfd delete transaction <transaction-id> application <application-id>
Sample YAML NGC AF PFD transaction configuration
The kube-cnca pfd apply expects the YAML configuration as in the format below. The file must contain the topmost configurations: apiVersion, kind, and policy. The configuration policy retains the NGC AF-specific transaction information.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ngc_pfd
policy:
pfdDatas:
- externalAppID: afApp01
allowedDelay: 1000
cachingTime: 1000
pfds:
- pfdID: pfdId01
flowDescriptions:
- "permit in ip from 10.11.12.123 80 to any"
domainNames:
- "www.google.com"
- pfdID: pfdId02
urls:
- "^http://test.example2.net(/\\S*)?$"
- pfdID: pfdId03
domainNames:
- "www.example.com"
- externalAppID: afApp02
allowedDelay: 1000
cachingTime: 1000
pfds:
- pfdID: pfdId03
flowDescriptions:
- "permit in ip from 10.68.28.39 80 to any"
- pfdID: pfdId04
urls:
- "^http://test.example1.net(/\\S*)?$"
- pfdID: pfdId05
domainNames:
- "www.example.com"
Sample yaml file for updating a single application:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ngc_pfd
policy:
pfdDatas:
- externalAppID: afApp01
allowedDelay: 1000
cachingTime: 1000
pfds:
- pfdID: pfdId01
flowDescriptions:
- "permit in ip from 10.11.12.123 80 to any"
- pfdID: pfdId02
urls:
- "^http://test.example2.net(/\\S*)?$"
- pfdID: pfdId03
domainNames:
- "www.latest_example.com"
Policy Authorization operations with 5G Core (through AF interface)
Supported operations through kube-cnca plugin:
- Creation of Policy Authorization - Application session context through the AF microservice.
- Deletion of application session context.
- Updating (patching) application session context.
- Get application session context.
- Update or delete Event Notification within an application session context.
Creation of the Policy Authorization Application session context is performed based on the configuration provided by the given YAML file. The YAML configuration should follow the provided sample YAML in the Sample YAML NGC AF transaction configuration section. Use the apply command as shown below to post an application session context creation request onto AF:
kubectl cnca policy-authorization apply -f <config.yml>
When the application session context is successfully created, the apply command will return the application session context ID (appSessionId). Only <appSessionId> should be used in further correspondence with AF concerning this particular application session context. It is the responsibility of the user to retain the <appSessionId> as kube-cnca is a stateless function.
To retrieve an existing AppSession Session Context with a known appSessionId, use:
kubectl cnca policy-authorization get <appSessionId>
To modify an active Application Session Context, use the patch command and provide a YAML file with the subset of the configuration to be modified:
kubectl cnca policy-authorization patch <appSessionId> -f <config.yml>
To delete an active Application Session Context, use the delete command as below:
kubectl cnca policy-authorization delete <appSessionId>
To add/modify Event Notification of active Application Session Context, use the subscribe command and provide a YAML file with the subset of the configuration to be modified:
kubectl cnca policy-authorization subscribe <appSessionId> -f <config.yml>
To unsubscribe from Event Notification of active Application Session Context, use the unsubscribe command:
kubectl cnca policy-authorization unsubscribe <appSessionId>
Sample YAML NGC AF Policy Authorization configuration
The kube-cnca policy-authorixation apply expects the YAML configuration as in the format below. The file must contain the topmost configurations: apiVersion, kind, and policy. The configuration policy retains the NGC AF-specific transaction information.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ngc_policy_authorization
policy:
afAppId: PolicyAuthAppId01
afRoutReq:
appReloc: true
routeToLocs:
- dnai: DNAI_RTL1
routeProfId: RouteInfo_ProfId01
routeInfo:
ipv4Addr: 196.168.0.1
ipv6Addr: 2001:db8:a0b:12f0::1
portNumber: 12345
spVal:
presenceInfoList:
- praId: PraId_01
presenceState: PRESENT
trackingAreaList:
- plmnId:
mcc: '010'
mnc: '101'
tac: tac02
ecgiList:
- plmnId:
mcc: '010'
mnc: '101'
eutraCellId: EutraCellId01
ncgiList:
- plmnId:
mcc: '010'
mnc: '101'
nrCellId: NrCellId01
globalRanNodeIdList:
- plmnId:
mcc: '010'
mnc: '101'
n3IwfId: N3IwfId01
gNbId:
bitLength: 32
gNBValue: GNB01
ngeNbId: NgeNbId
tempVals:
- startTime: '10:30'
stopTime: '11:30'
- startTime: '12:30'
stopTime: '13:30'
upPathChgSub:
notificationUri: http://example.com/notif
notifCorreId: '1234'
dnaiChgType: EARLY
evSubsc:
events:
- event: PLMN_CHG
notifMethod: EVENT_DETECTION
notifUri: www.example.com
usgThres:
duration: 100
totalVolume: 1000
downlinkVolume: 500
uplinkVolume: 200
medComponents:
- afAppId: MC_AppId01
afRoutReq:
appReloc: true
routeToLocs:
- dnai: EARLY
routeProfId: RouteInfo_ProfId02
routeInfo:
ipv4Addr: 196.168.0.1
ipv6Addr: 2001:db8:a0b:12f0::1
portNumber: 12345
spVal:
presenceInfoList:
- praId: PraId_01
presenceState: PRESENT
trackingAreaList:
- plmnId:
mcc: '010'
mnc: '101'
tac: tac01
ecgiList:
- plmnId:
mcc: '010'
mnc: '101'
eutraCellId: EutraCellId01
ncgiList:
- plmnId:
mcc: '010'
mnc: '101'
nrCellId: NrCellId02
globalRanNodeIdList:
- plmnId:
mcc: '010'
mnc: '101'
n3IwfId: N3IwfId01
gNbId:
bitLength: 32
gNBValue: GNB01
ngeNbId: NgeNbId
tempVals:
- startTime: '13:30'
stopTime: '14:30'
- startTime: '15:30'
stopTime: '16:30'
upPathChgSub:
notificationUri: http://example.com/notif_mc
notifCorreId: '4321'
dnaiChgType: EARLY
contVer: 123
medCompN: 1
dnn: PolicyAuthDnn01
ipDomain: PolicyAuthIPDomain
notifUri: http://afservice:9050/policyAuthorizationNotif
sliceInfo:
sst: 100
sd: PolicyAuthSd_01
suppFeat: 1
ueIpv4: 127.0.0.1
Traffic Influence Subscription description
This section describes the parameters that are used in the Traffic Influence subscription POST request. Groups mentioned as mandatory must be provided; in the absence of the mandatory parameters, a 400 response is returned.
Identification (Mandatory)
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| afTransId | Identifies an NEF Northbound interface transaction, generated by the AF |
| self | Link to this resource. This parameter shall be supplied by the NEF in HTTP POST responses, which is used by AF for further operations |
Traffic Description Group (Mandatory)
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| afServiceId | Identifies a service on behalf of which the AF is issuing the request |
| dnn | Identifies a DNN |
| snssai | Identifies an S-NSSAI |
NOTE: One of afServiceId or dnn shall be included
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| afAppId | Identifies an application |
| trafficFilters | Identifies IP packet filters |
| ethTrafficFilters | Identifies Ethernet packet filters |
NOTE: One of “afAppId”, “trafficFilters”, or “ethTrafficFilters” shall be included
Target UE Identifier (Mandatory)
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| externalGroupId | Identifies a group of users |
| anyUeInd | Identifies whether the AF request applies to any UE. This attribute is set to “true” if applicable for any UE. Otherwise, set to “false” |
| gpsi | Identifies a user |
| ipv4Addr | Identifies the IPv4 address |
| ipv6Addr | Identifies the IPv6 address |
| macAddr | Identifies the MAC address |
NOTE: One of individual UE identifiers (“gpsi”, “ipv4Addr”, “ipv6Addr” or macAddr), External Group Identifier (“externalGroupId”) or any UE indication “anyUeInd” shall be included
Application Relocation (Optional)
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| appReloInd | Identifies whether an application can be relocated once a location of the application has been selected. Set to “true” if it can be relocated; otherwise, set to “false”. The default value is “false” if omitted |
Traffic Routing (Optional)
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| trafficRoutes | Identifies the N6 traffic routing requirement |
Spatial Validity (Optional)
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| validGeoZoneIds | Identifies a geographic zone that the AF request applies only to the traffic of UE(s) located in this specific zone |
Temporal Validity (Optional)
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| tempValidities | Indicates the time interval(s) during which the AF request is to be applied |
UPF Event Notifications (Optional)
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| subscribedEvents | Identifies the requirement to be notified of the event(s) |
| dnaiChgType | Identifies a type of notification regarding UP path management event |
| notificationDestination | Contains the Callback URL to receive the notification from the NEF. It shall be present if the “subscribedEvents” is present |
AF to NEF specific (Optional)
| Attribute name | Description |
|---|---|
| suppFeat | Indicates the list of Supported features used as described in subclause 5.4.4. This attribute shall be provided in the POST request and in the response of successful resource creation. Values 1 - Notification_websocket 2 - Notification_test_event |
| requestTestNotification | Set to true by the AF to request the NEF to send a test notification as defined in subclause 5.2.5.3 of 3GPP TS 29.122 [4]. Set to false or omitted otherwise |
| websockNotifConfig | Configuration parameters to set up notification delivery over Websocket protocol |
Packet Flow Description transaction description
This sections describes the parameters that are used in the Packet flow description POST request. Groups mentioned as mandatory must be provided; in the absence of the Mandatory parameters, a 400 response is returned.
| Attribute name | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
| externalAppID | Yes | Unique Application identifier of a PFD |
| Allowed Delay | No | Indicates that the list of PFDs in this request should be deployed within the time interval indicated by the Allowed Delay |
| Caching Time | No | It shall be included when the allowed delayed cannot be satisfied (i.e., it is smaller than the caching time configured in fetching PFD) |
| pfdId | Yes | Identifies a PFD of an application identifier. |
| flowDescriptions | NOTE | Represents a 3-tuple with protocol, server ip, and server port for UL/DL application traffic. |
| Urls | NOTE | Indicates a URL or a regular expression that is used to match the significant parts of the URL. |
| domainName | NOTE | Indicates an FQDN or regular expression as a domain name matching criteria. |
NOTE: One of the attributes of flowDescriptions, URls, and domainName is mandatory.
Policy Authorization Application Session Context description
This section describes the parameters that are used in the AppSessionContextReqData part of Policy Authorization POST request. Groups mentioned as mandatory must be provided; in the absence of the Mandatory parameters, a 400 response is returned.
| Attribute name | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|
| suppFeat | Yes | This provides a list of supported features used as described Individual Application Session Context resource. Supported features are: (a) InfluenceOnTrafficRouting (b) SponsoredConnectivity (c) MediaComponentVersioning. |
| notifUri | Yes | Notification URI for Application Session Context termination requests. |
| afRoutReq | Conditional | Indicates the AF traffic routing requirements. It shall be included if Influence on Traffic Routing feature is supported. Applicable when suppFeat indicates InfluenceOnTrafficRouting |
| dnn | Conditional | Data Network Name. Applicable when suppFeat indicates InfluenceOnTrafficRouting and afRoutReq is present |
| aspId | Conditional | Application service provider identity. It shall be included if “SponsoredConnectivity” feature is supported |
| sponId | Conditional | Sponsor identity. It shall be included if the “SponsoredConnectivity” feature is supported. |
| sponStatus | Optional | Indication of whether sponsored connectivity is enabled or disabled/not enabled |
| contVer | Conditional | Represents the content version of a media component. |
| ueIpv4 | Optional | The IPv4 address of the served UE. |
| ueIpv6 | Optional | The IPv6 address of the served UE. |
| ueMac | Optional | The MAC address of the served UE. |
NOTE: Only one of the attributes of ueIpv4, ueIpv6, and ueMAC is mandatory.